The rsyslog Evolution: Bridging BSD Heritage with Adiscon Innovation
It is a well-documented fact in the open-source community that rsyslog traces its lineage back to the original 1980s BSD syslogd developed by Eric Allman, primarily through the sysklogd fork. This foundation provided the industry with a standardized way to communicate system events for decades.
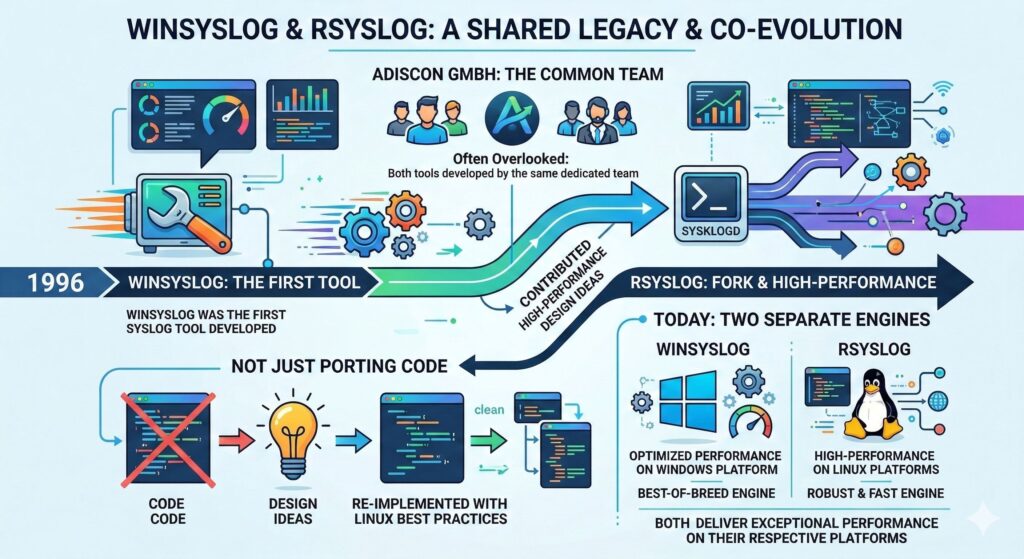
However, even before the digital landscape evolved into the era of high-velocity data, the original single-threaded BSD design was known by us to face significant performance bottlenecks. As such, we were well aware of the need to support multithreading.
Continue reading “The rsyslog Evolution: Bridging BSD Heritage with Adiscon Innovation”Docs moved to new Domain
We have today moved the rsyslog official documentation to https://docs.rsyslog.com/doc instead of our long-standing location directly on www.rsyslog.com/doc. All existing links will be properly redirected. The goal is to keep the all-important doc set on its own resource, which helps with scaling and ensuring availability of the documentation.
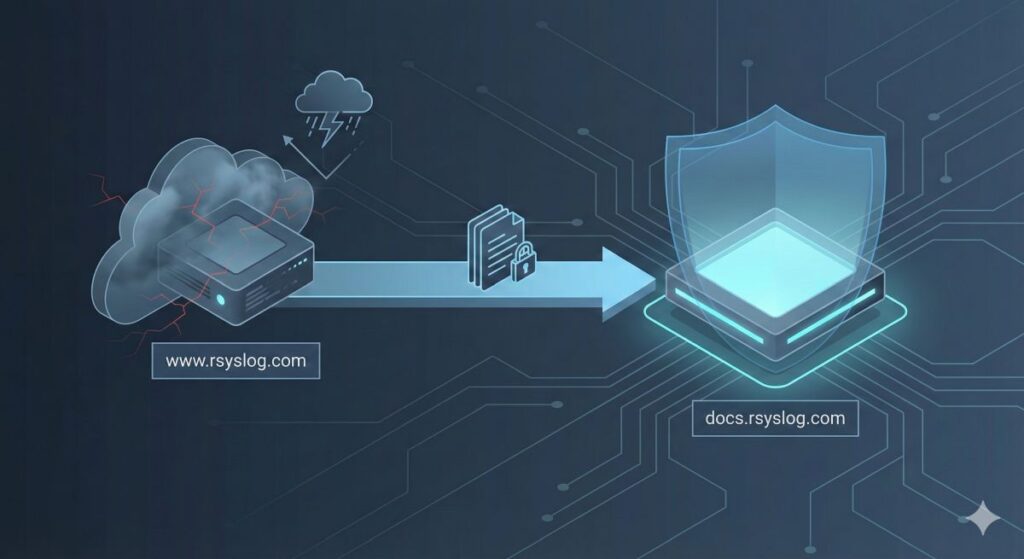
This move was considered for quite a while and has its pros and cons. The ultimate reason we are doing it, and doing it now is a cyberattack against rsyslog.com which began four days ago. While we mitigated it quickly, it led to unavailability of the doc for around one hour. That made us finally make the decision to move doc to a dedicated system, which we can make more robust than the full featured site with it’s dynamic content.
Continue reading “Docs moved to new Domain”rsyslog 8.2602.0: ROSI Collector, rate-limit policies, stronger TLS, and telemetry integration
We have released rsyslog 8.2602.0, the February 2026 scheduled-stable version. Scheduled-stable releases are bi-monthly snapshots of the daily-stable branch, providing predictable update points with the same functional content as daily-stable at the time of the snapshot.
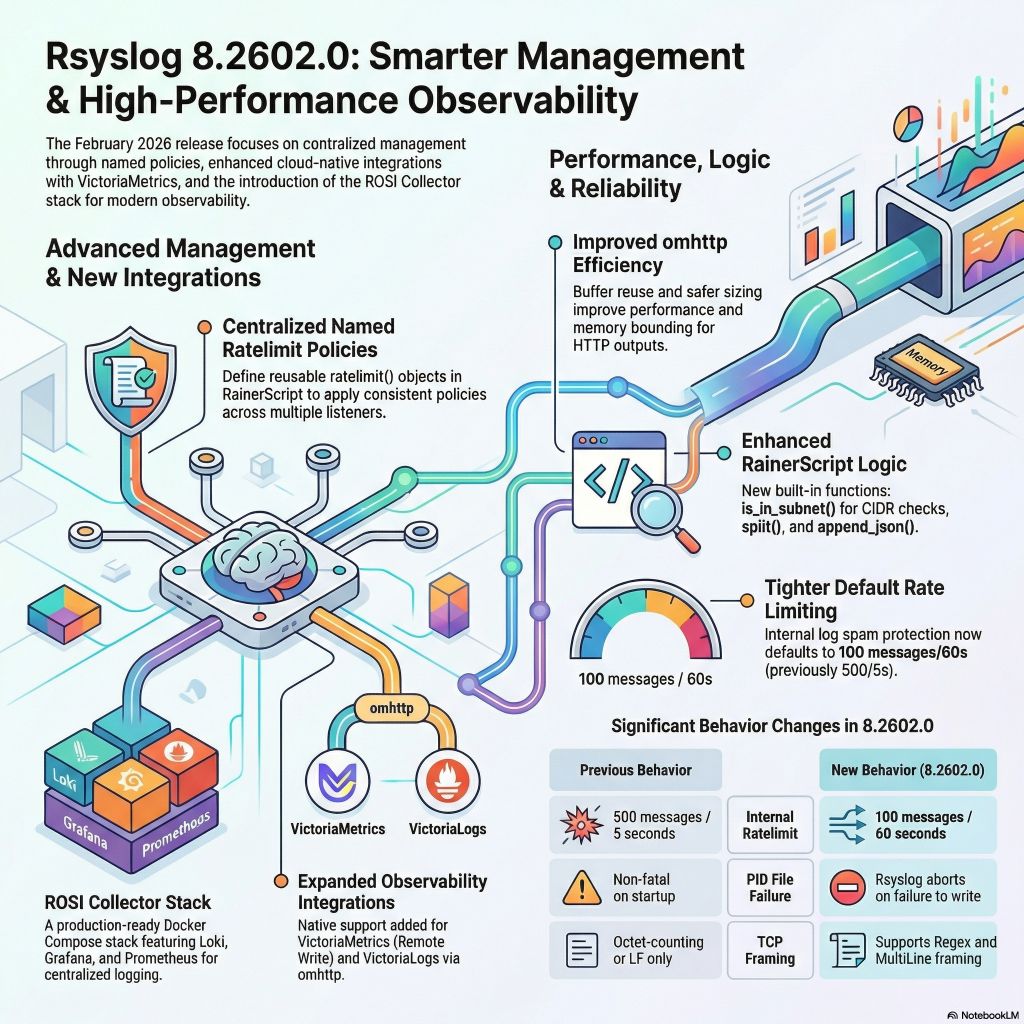
This release introduces a new production-ready deployment stack and continues significant runtime and security hardening.
Four major highlights:
- ROSI Collector: centralized log collection stack
- Named rate limit policies for imtcp and imptcp
- Security and TLS hardening
- Telemetry and ecosystem integration
What rsyslog is today: a high-performance log ingestion and ETL engine
The site title and GitHub project tagline now describe rsyslog as a high-performance log ingestion and ETL engine.
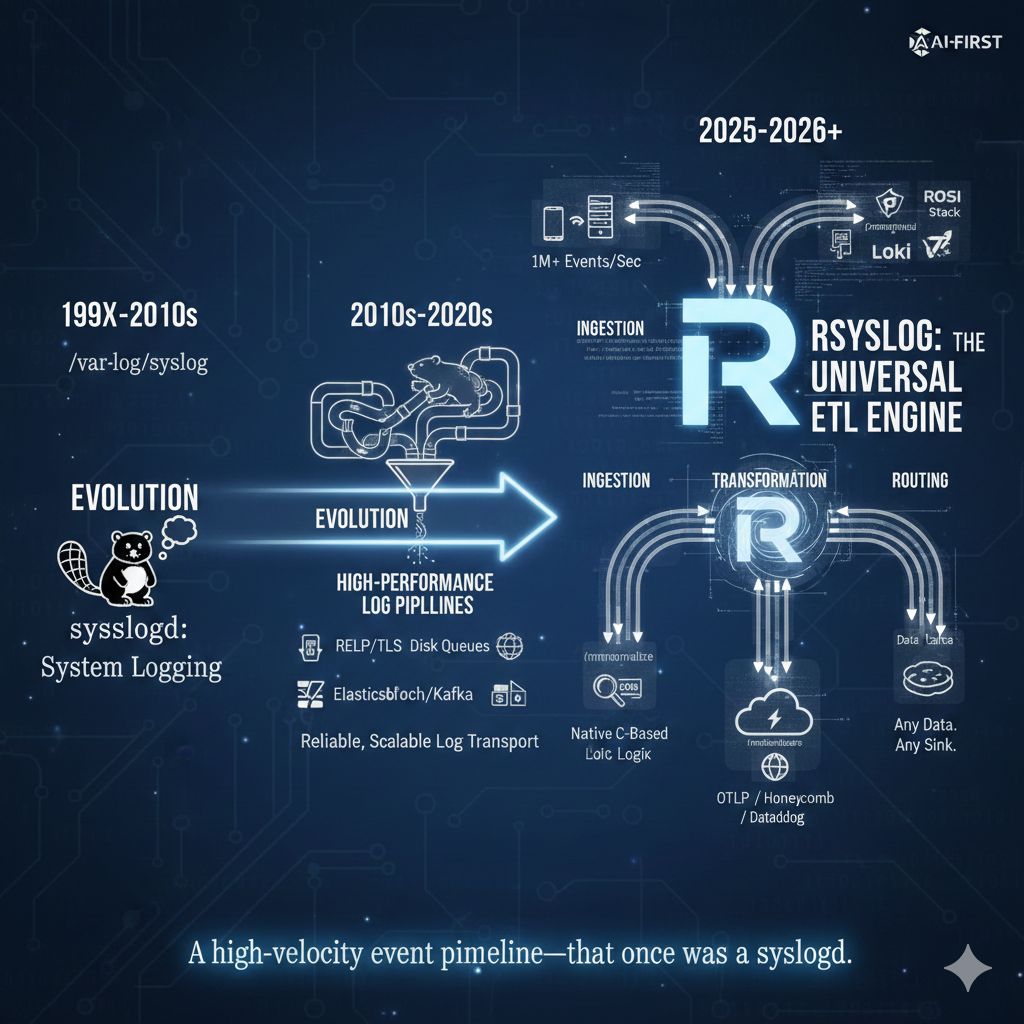
This is a small but visible change. It reflects how rsyslog is actually used today in modern infrastructures, and it aligns the project’s public description with long-standing technical reality. It is not a rebranding exercise, and it does not change what rsyslog is compatible with or where it comes from.
If you have followed the project for a long time, the wording may stand out. That is intentional. It acknowledges an evolution that has been underway for years and that many users already rely on in production.
Continue reading “What rsyslog is today: a high-performance log ingestion and ETL engine”imfile inotify handling improved: safer systems, lower rsyslog impact
Large imfile deployments can put pressure on Linux inotify resources. In practice, running out of inotify watches is very uncommon, but when it does happen, the consequences used to be unpleasant and system-wide.
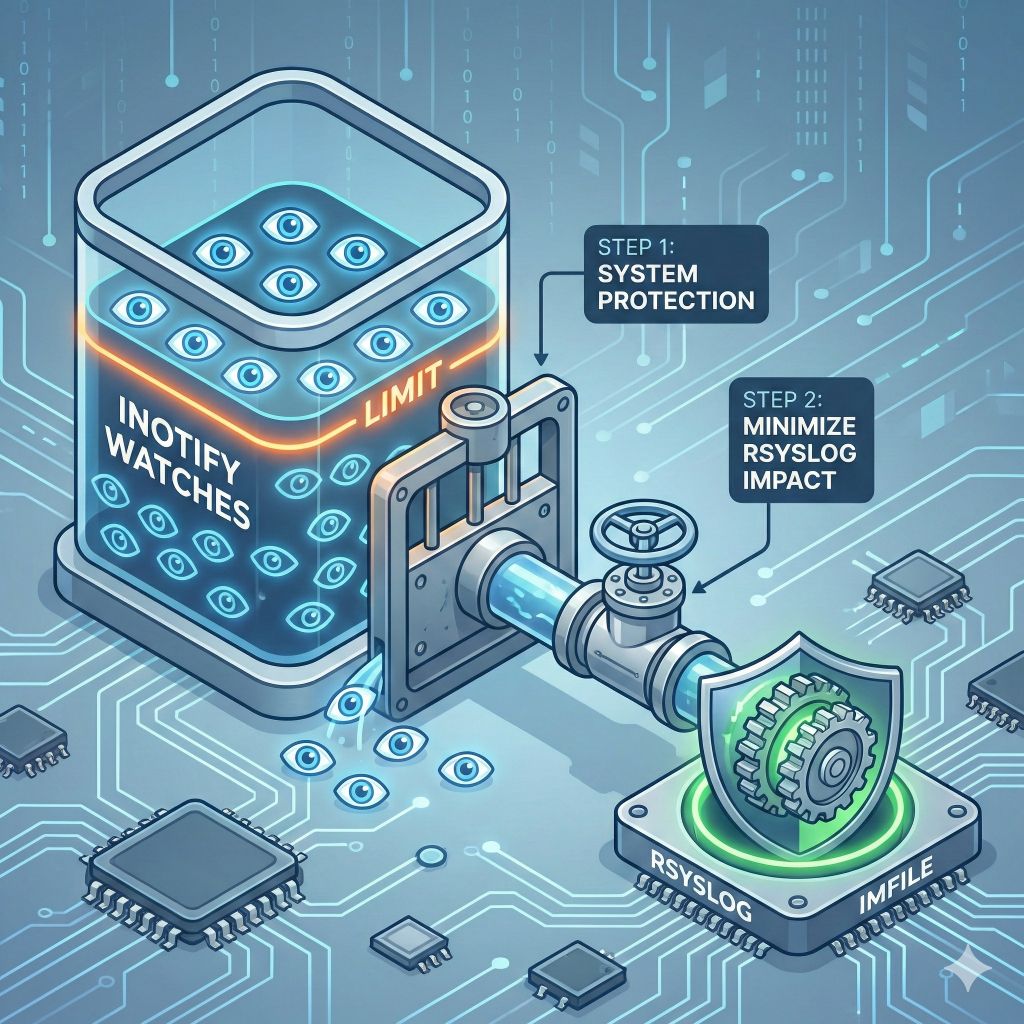
To address this properly, we completed a single improvement delivered in two steps: treat inotify usage as a bounded, shared system resource while keeping rsyslog itself as unaffected as possible.
Continue reading “imfile inotify handling improved: safer systems, lower rsyslog impact”Call for Experiments: Agentic Coding on rsyslog
We are inviting developers, junior engineers, and curious “vibe coders” to experiment with AI code agents on a real production code base: rsyslog.

This is not a sandbox or demo repository. This is mature infrastructure software with real users, strict quality requirements, and a long maintenance history.
If you want to see how far agentic coding really goes, this is a good place to try.
Continue reading “Call for Experiments: Agentic Coding on rsyslog”New: production-ready observability stack integrated into rsyslog
Rsyslog now includes an officially maintained, production-oriented observability stack for centralized logging and monitoring. The stack is designed as a practical reference deployment that can be used directly or adapted to local requirements.
This addition was merged into the rsyslog main branch last Friday via pull request #6325.
The stack is called ROSI, short for Rsyslog Operations Stack Initiative. Its first deliverable, the ROSI Collector, focuses on the central log collection side.
What is included
The ROSI Collector is shipped as a Docker Compose deployment located under:
deploy/docker-compose/rosi-collector/It combines the following components into a coherent setup:
- rsyslog as a centralized log receiver
- Grafana Loki for log storage and querying
- Prometheus for metrics collection
- Grafana with preconfigured dashboards
- Traefik as a reverse proxy with automatic TLS via Let’s Encrypt
The stack is intended to be directly usable while remaining fully transparent and modifiable.
Core properties
- Reference deployment, not a demo
The configuration reflects operational practice and recommended integration patterns rather than a minimal showcase. - Secure transport
Syslog reception over TLS (RFC 5425) is supported, including mTLS. Certificate generation helpers are included. - Immediate observability
Predefined Grafana dashboards provide visibility into log flow, system state, and basic operational metrics without additional wiring. - Operational helpers
Scripts are included for certificate handling, stack status checks, and Prometheus target management. - Integrated documentation
Documentation is part of the main rsyslog documentation.
Why this exists
Many users want a complete and coherent logging and observability setup instead of assembling individual components themselves. The ROSI Collector provides a known-good baseline that can be deployed as-is or adjusted incrementally.
For the rsyslog project, ROSI establishes an explicit operational reference. This improves consistency across documentation, support, and future observability-related work, without changing rsyslog’s role as a flexible and modular logging engine.
Scope and future direction
The current ROSI Collector targets VM-based and single-host Docker environments. These setups are common and often favor solutions that are understandable, inspectable, and low in operational complexity.
ROSI is expected to evolve. Kubernetes support is a targeted extension, but intentionally not part of the initial merge. Establishing a solid and well-understood baseline takes priority over covering all deployment models at once.
The rsyslog 2025 Year in Review
Evolving Proven Infrastructure for a New Era
The year 2025 was a defining year for rsyslog. Not because of a single feature or release, but because several long-running threads finally converged: AI-assisted workflows, even fuller multi-core scalability, and native integration with modern observability stacks.

Rather than chasing trends, rsyslog focused on evolving what it already does best: reliable, high-performance log and data processing for real-world infrastructure.
At the same time, the project continued a shift that has been underway for years. For quite some time now, rsyslog has been more than a syslog daemon. It is increasingly used as a flexible, programmable data and information pipeline that happens to excel at logs.
Continue reading “The rsyslog 2025 Year in Review”Season’s Greetings from the rsyslog Project
As the year comes to a close, we would like to send our warm thanks to everyone who makes the rsyslog project what it is.

To our users, contributors, and community members around the world: thank you for your trust, feedback, bug reports, patches, documentation work, and thoughtful discussions throughout the year. Open source only works because of people who care, and rsyslog is no exception.
Continue reading “Season’s Greetings from the rsyslog Project”Native OpenTelemetry Export Arrives: Introducing the omotlp Output Module
With the latest merge into the rsyslog development branch, rsyslog now provides a native OpenTelemetry (OTLP/HTTP) log exporter. The new omotlp output module enables rsyslog to send logs directly to any OTLP-compliant collector without the need for sidecars or protocol translators.
This is Phase 1 of the OpenTelemetry integration. It focuses on the OTLP/HTTP JSON transport, including batching, retry semantics, TLS/mTLS, and proxy support. Additional transport variants (gRPC and HTTP/protobuf) may follow in future phases.
Continue reading “Native OpenTelemetry Export Arrives: Introducing the omotlp Output Module”